
Tutorial
The tutorial of BGMP is as following:
- 1. Overview of BGMP
- 2. Browse BGMP
- 3. Advanced search
- 4. Submit data
- 5. Functional Prediction
- 6. Data download
- 7. Contact
What the Database Is?
This database encompasses detailed information on the platelet blood group system, red blood cell blood group system, granulocyte blood group system, and serum protein blood group system. It is designed to provide researchers and clinicians with a comprehensive platform for querying and analyzing relevant data, including antigen expression, genetic mutations, and polymorphisms within these blood group systems.
How the Database Is Made?
The construction of the database involves collecting relevant information from scientific literature and clinical data, followed by standardizing and formatting the data. The data will be entered into the database in a unified format to facilitate efficient querying and usage. The database structure will be designed to ensure easy retrieval of information and provide a user-friendly interface for convenient data access.
What the Database Means?
The database will advance research into blood group systems, support more precise scientific investigations, and assist clinicians in developing more effective treatment plans, thereby reducing complications in transfusions and transplants. Additionally, it will promote global data sharing and collaboration, enhancing research efficiency and improving medical standards.
Here is the usage guide for the database (using the ABO blood group system as an example):
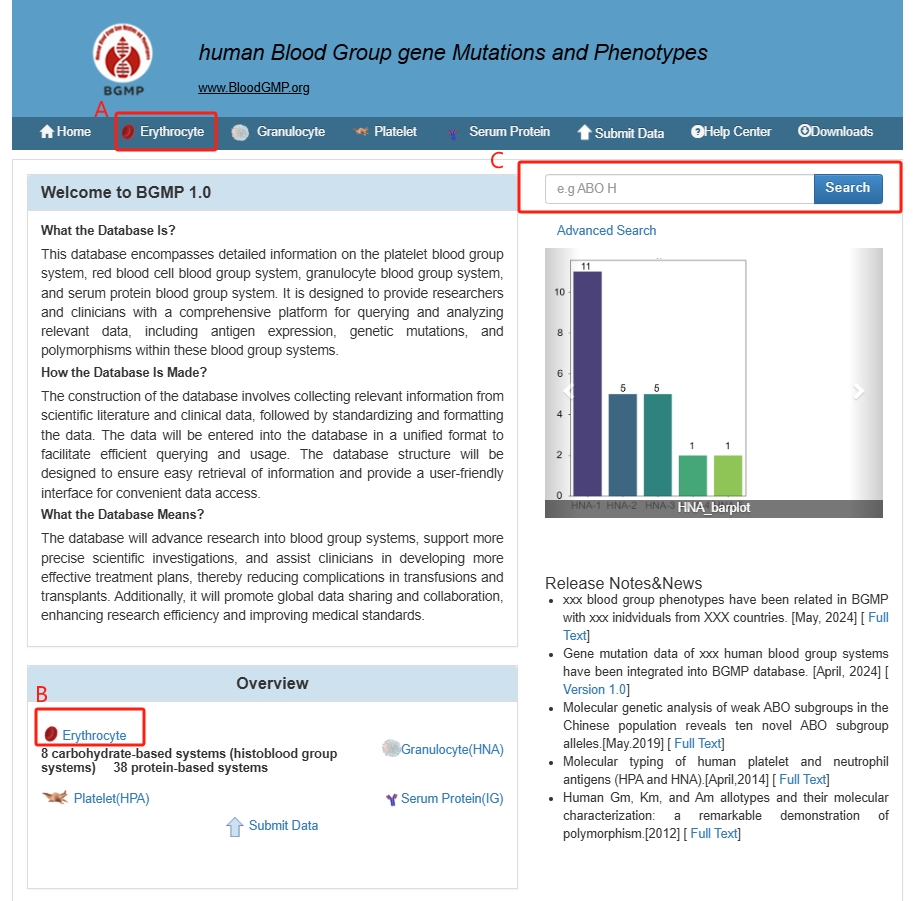
2.1 Users can access the corresponding page through the tabs at the top of the page or the "Overview" (A or B) tab, or they can use the quick search (C) to enter keywords of interest for searching.
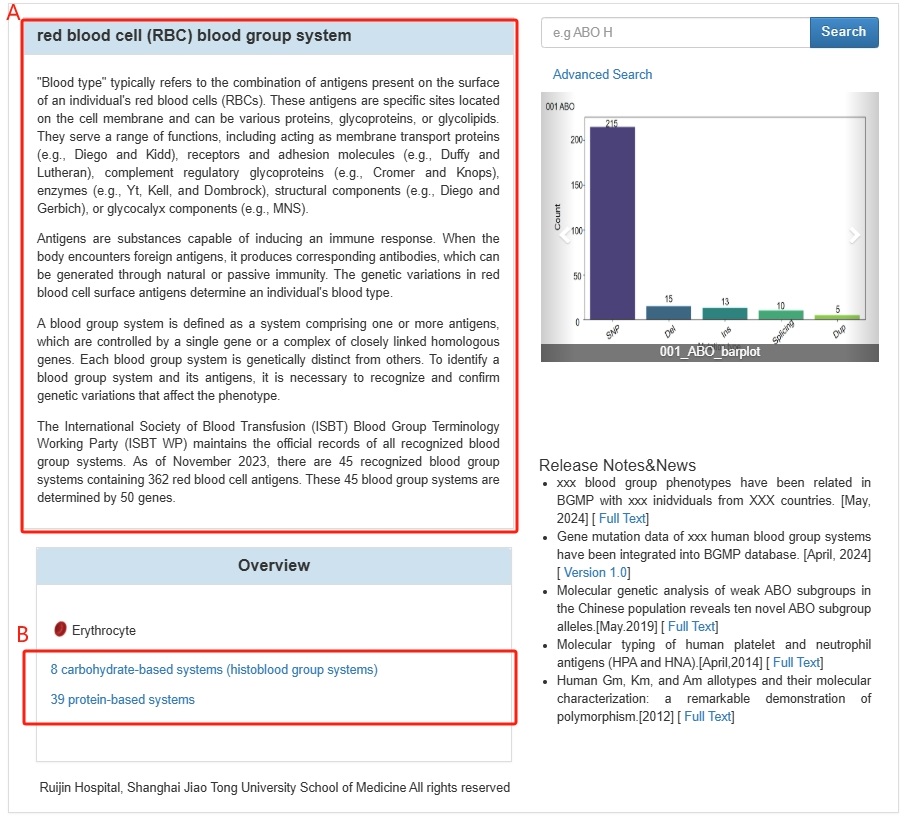
2.2 After entering the corresponding page, users will see an introduction to the relevant
blood group
system (A) and the
47 erythrocyte blood group systems (B), which are categorized into two types: carbohydrate-based
systems (histoblood
group systems) and 39 protein-based systems.
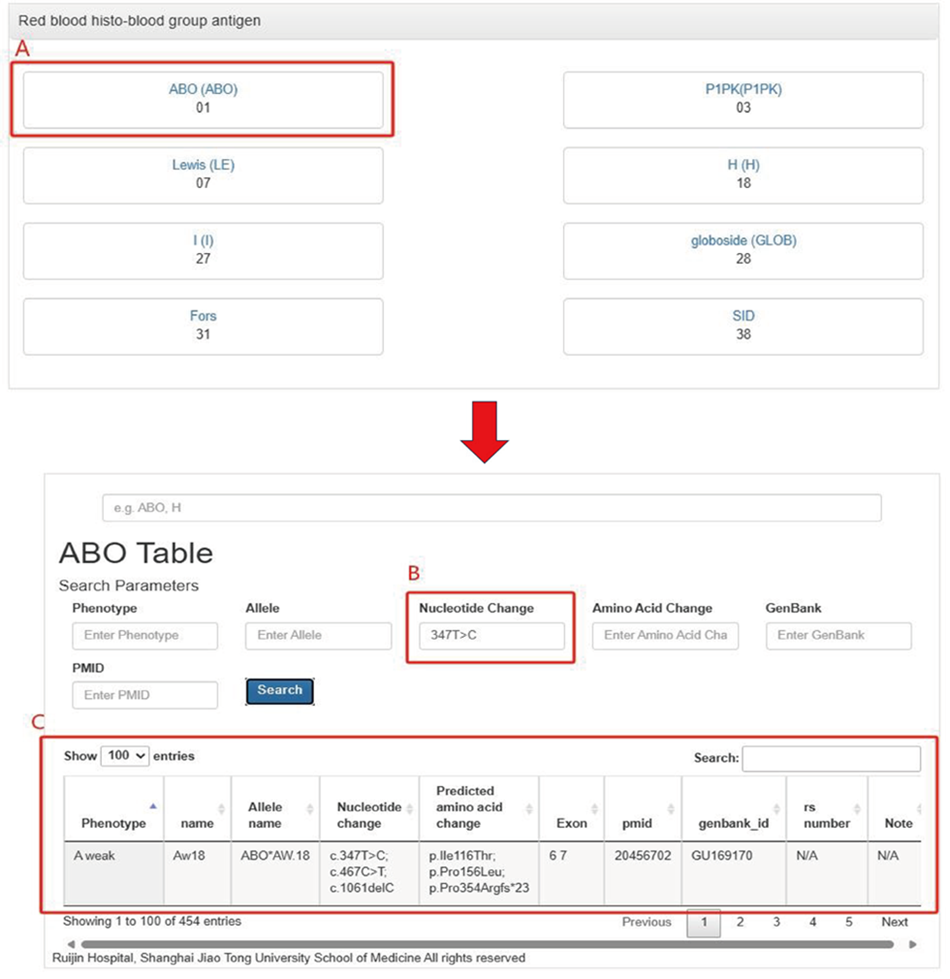
2.3 By clicking again, you can enter the corresponding blood group system (A), input
relevant
information (such as
phenotype, alleles, nucleotide changes, amino acid changes, etc.) for the search (B), and retrieve
the related results
(C).
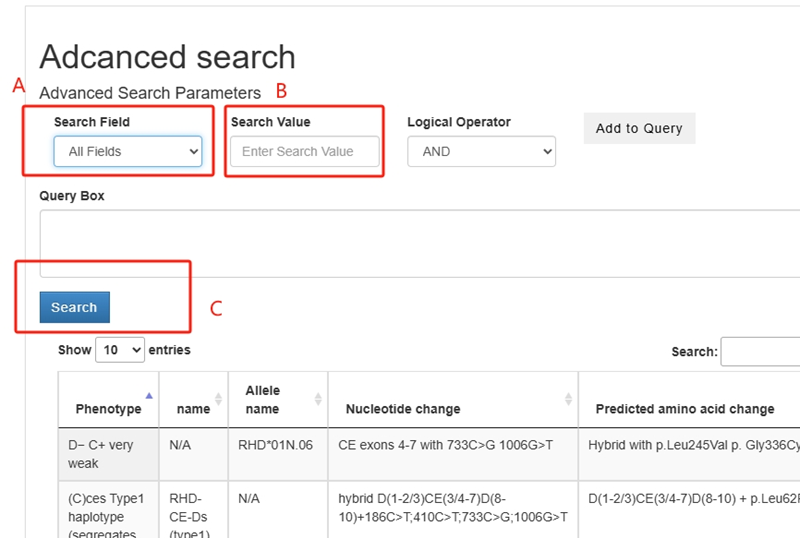
You can access the advanced search interface by clicking the "Advanced" button below the quick search key. In box A, you can select different types, including Phenotype, Allele, Nucleotide Change, and Amino Acid Change. In box B, enter the corresponding search information. You can use the "And" button to add additional relevant information. Once you have finished adding the information, click button C to perform the search.
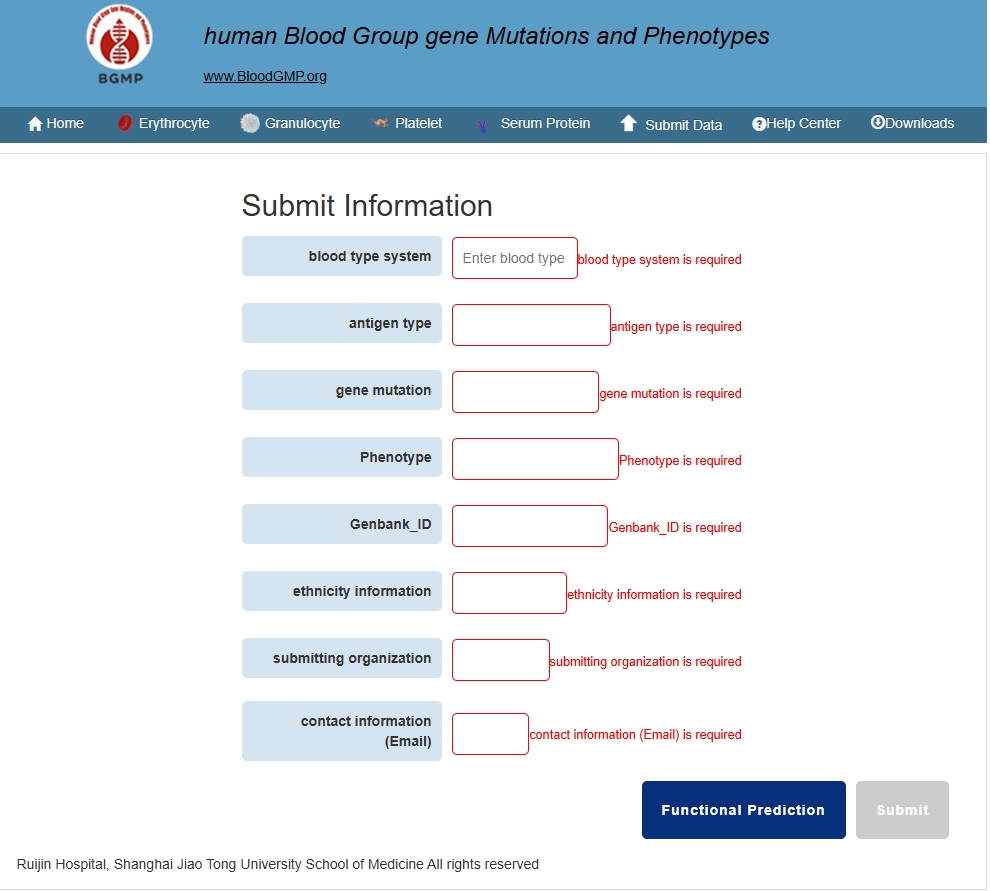
Data submission can be accessed by clicking "Submit Data" at the top of the browser to enter the data submission page (A). On this page, you need to enter information such as blood type system, antigen type, gene mutation, phenotype, GenBank ID, and ethnicity information. In addition, you should also provide the submitting organization and contact information for follow-up communication.In addition, you can access the PolyPhen-2 protein function prediction interface by clicking on "Functional Prediction".
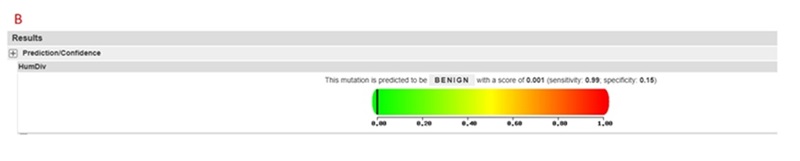
Click on the "Functional Prediction" tab to enter interface A. After entering the mutation information, proceed with the prediction. The results will be displayed as shown in interface B.
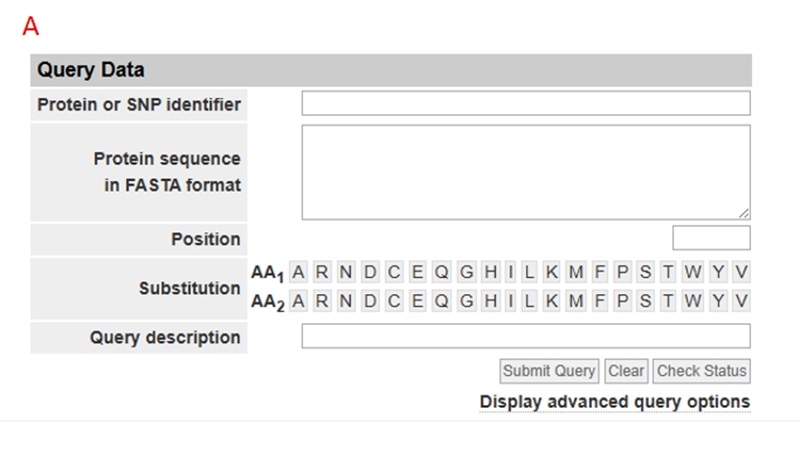
Prediction results classification: Benign: Indicates that the mutation is likely to have no significant impact on protein function. Possibly Damaging: Indicates that the mutation may have some impact on protein function. Probably Damaging: Indicates that the mutation is likely to have a significant impact on protein function. Score: The model calculates a score ranging from 0 to 1. The higher the score, the greater the potential impact of the mutation on protein function.
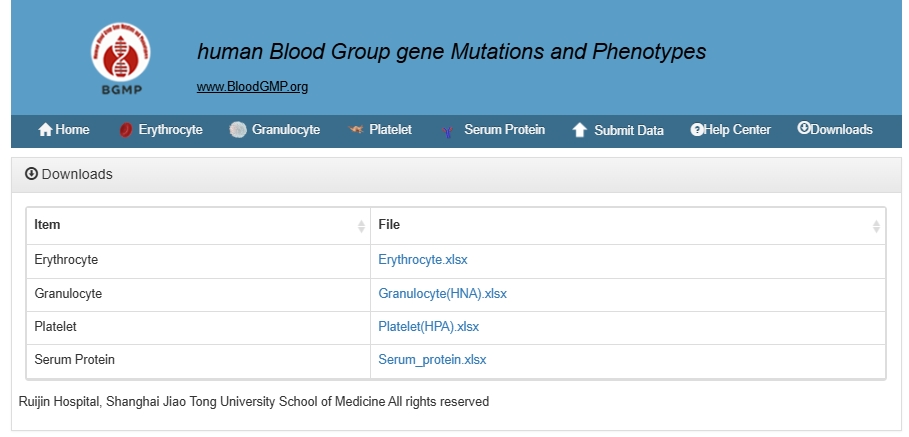
Users can download the raw data on the Download page.
Organization: Department of Transfusion Medicine, Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine
Contact: Cai Xiaohong
Email: BloodGMP@163.com